Diagnosis of rheumatic heart disease
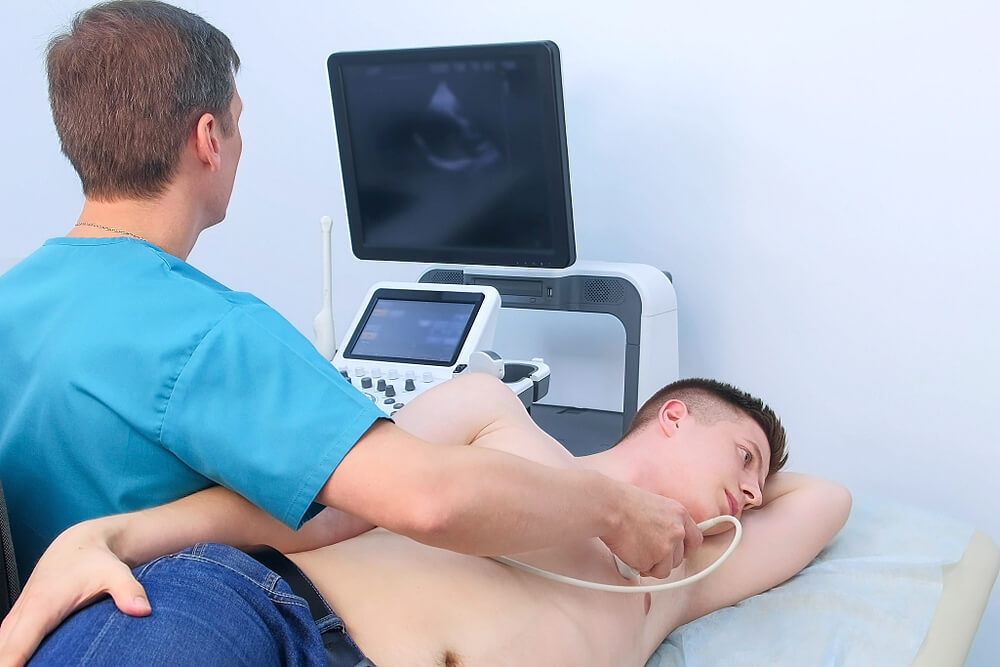
Your doctor diagnoses you depending on some factors. Your doctor will ask you about the symptoms that may make him suspect the disease. Also, your doctor looks for rheumatic fever because it is the direct cause of rheumatic heart disease. You should have one major and two minor criteria to confirm your diagnosis. Your doctor will ask you to do some investigations:
1- Blood tests: usually, the patient with rheumatic heart disease has a streptococcal infection, so the blood picture show leukocytosis, elevated ESR, and elevated C-reactive protein.
2- Echocardiogram: Your doctor uses sound waves to check the heart valves. Echocardiogram show enlargement of heart chambers and damage of heart valves.
3- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Your doctor uses ECG to detect the electrical activity of your heart. ECG shows an irregular rhythm and damage to heart valves. Also, ECG can show chamber enlargement and pulmonary hypertension.
4- Chest X-Ray: your doctor uses the X-Ray to check the lung and heart. The X-Ray shows pulmonary congestion and chamber enlargement.


