The surgical procedure
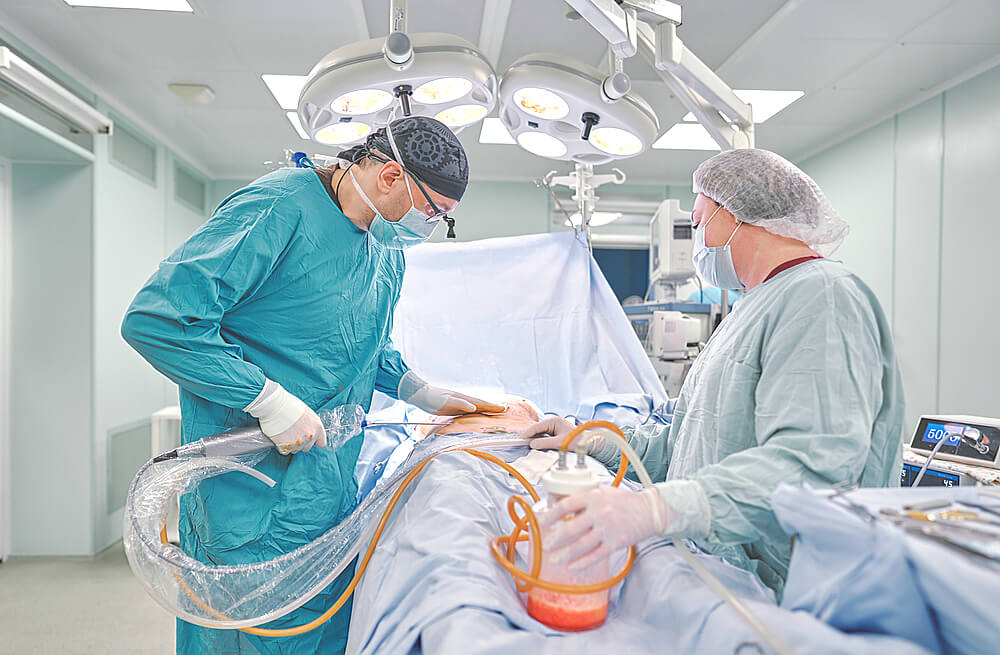
The liposuction surgery usually undergoes under general anesthesia to control the patient position during the procedure, and to decrease the level of lidocaine to prevent subsequent lidocaine toxicity.
During fluid infiltrate, the patient’s body should be kept warm by thermal blanket, to protect against hypothermia.
The patient skin is prepared by scrubbing it with iodine solution to ensure sterile surface, and do not cause later infection. For prophylaxis, antibiotic therapy should be started twenty-four hours before the surgery.
There are four types of liposuction techniques. The techniques are tumescent liposuction, dry liposuction, wet liposuction, and superwet liposuction. The main difference between these techniques is the amount of tissue infiltrate, and the expected blood loss.
1. Dry liposuction
In this technique, there is no fluid injected into the adipose tissue, and it is mostly used in small volume liposuction. Around 30% of the aspiration during the procedure is blood.
2. Wet liposuction
In this technique, first, around 100-300 cm of fluid is infiltrated into the subcutaneous fat in the specific sites that would be later suctioned. The amount of aspirated blood is less than the dry technique. Adding epinephrin to the infiltrating tissue can decrease the amount of aspirated blood to less than 15% of the aspirated volume.
3. Superwet liposuction
This technique was developed in the late eighties. First a solution consists of equal parts of epinephrin, and local anesthesia is infiltrated to the subcutaneous fat before suctioning it later. This technique causes dramatic decrease in the aspirated blood to reach 2% of the total volume aspirated.
4. Tumescent liposuction
In this technique, lidocaine and epinephrin are directly injected into the subcutaneous fat just before the procedure. The blood loss is approximately 1% of the aspirated volume. Recently, most plastic surgeon use mix of both superwet, and tumescent techniques.


